In addition, changes in prices and industry trends can make historical data an unreliable predictor of future overhead costs. Finally, using a predetermined overhead rate can result in inaccurate decision-making if the rate is significantly different from how to calculate predetermined overhead rate the actual overhead cost. Big businesses may actually use different predetermined overhead rates in different production departments, as these may vary significantly. By having multiple rates like this, you can achieve a greater degree of accuracy.
Practical Application of Overhead Rates in Business
All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. This calculation acts as a tool for timely reviews of spending, helping to trigger necessary adjustments in expense management in relation to changes in production or sales. For insights on optimizing business expenses, explore our guide on cost management strategies. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries.
Our Team Will Connect You With a Vetted, Trusted Professional
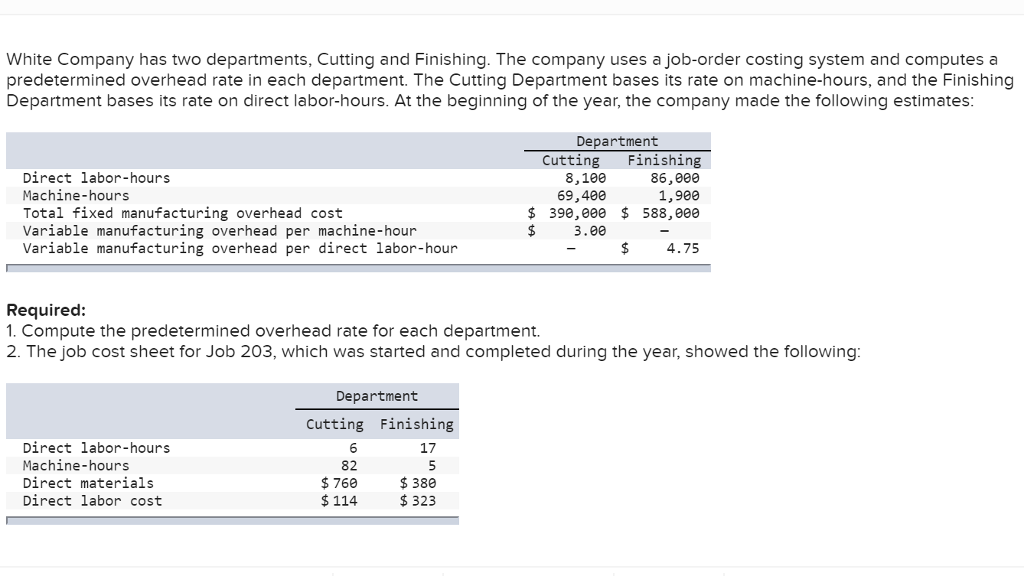
However, estimating does not involve predicting or forecasting instead it only involves quantifying for an interval of time. Traditionally, overheads have been absorbed in the product cost based on a single basis of apportionment. For instance, in a labor-intensive environment, labor hours were used to absorb overheads. On the other hand, the machine hours were used to absorb overheads in a machine incentive environment. Predetermined overhead is an estimated rate used by the business to absorb overheads in the product cost, and it’s calculated by dividing overheads by the budgeted level of activity.
Understanding Goodwill in Balance Sheet – Explained
Hence, one of the major advantages of predetermined overhead rate formula is that it is useful in price setting. Calculating the predetermined overhead rate is crucial for accurate cost accounting and managerial decision-making. This rate, calculated as total estimated overhead costs / total estimated allocation base, helps businesses in allocating overhead costs more precisely. Whether determining product costs or assessing profitability, understanding this rate is fundamental.
Income Statement Under Absorption Costing? (All You Need to Know)
- Unlock the power of Sourcetable, an AI-driven spreadsheet that revolutionizes the way you perform calculations.
- This means that for every hour of work the marketing agency performs, it will incur $20 in overhead costs.
- Obotu has 2+years of professional experience in the business and finance sector.
- Nonetheless, it is still essential for businesses to reconcile the difference between the actual overhead and the estimated overhead at the end of their fiscal year.
However, there is a strong need to constantly update the production level depending on the seasonal fluctuations and the factor affecting the demand of the product. We’re a headhunter agency that connects US businesses with elite LATAM professionals who integrate seamlessly as remote team members — aligned to US time zones, cutting overhead by 70%. Let’s say we want to calculate the overhead cost of a homemade candle ecommerce business. Then, they’ll need to estimate the amount of activity or work that will be performed in that same time period.
The use of predetermined overheads effectively incorporates the cost effects of seasonal variations in the product cost and price. However, the problem with absorption/traditional costing is that we have to ignore individual absorption bases and absorb all overheads using a single level of activity. Hence, this is a compromise on the accuracy of the overall allocation process. On the other hand, the ABC system is more complex and requires extensive administrative work. It’s also important to note that budgeted figures in calculating overhead rates are used due to seasonal fluctuation/expected changes in the external environment.
This involves categorizing all overhead costs and regularly analyzing them to identify potential savings. Analyzing overhead rates by department in this manner helps identify problem areas and opportunities to improve profitability. By factoring in overhead costs in this manner, the company arrives at a more accurate COGS.
It’s then further allocated to the departments that use the procurement facility. Further, overhead estimation is useful in incorporating seasonal variation and estimate the cost at the start of the project. Detailed cost analysis helps to estimate the cost of overheads with accuracy. Further, customized input from different departments can be obtained to enhance the accuracy of the budget. Keeping overhead costs in check can have a notable impact on the bottom line.
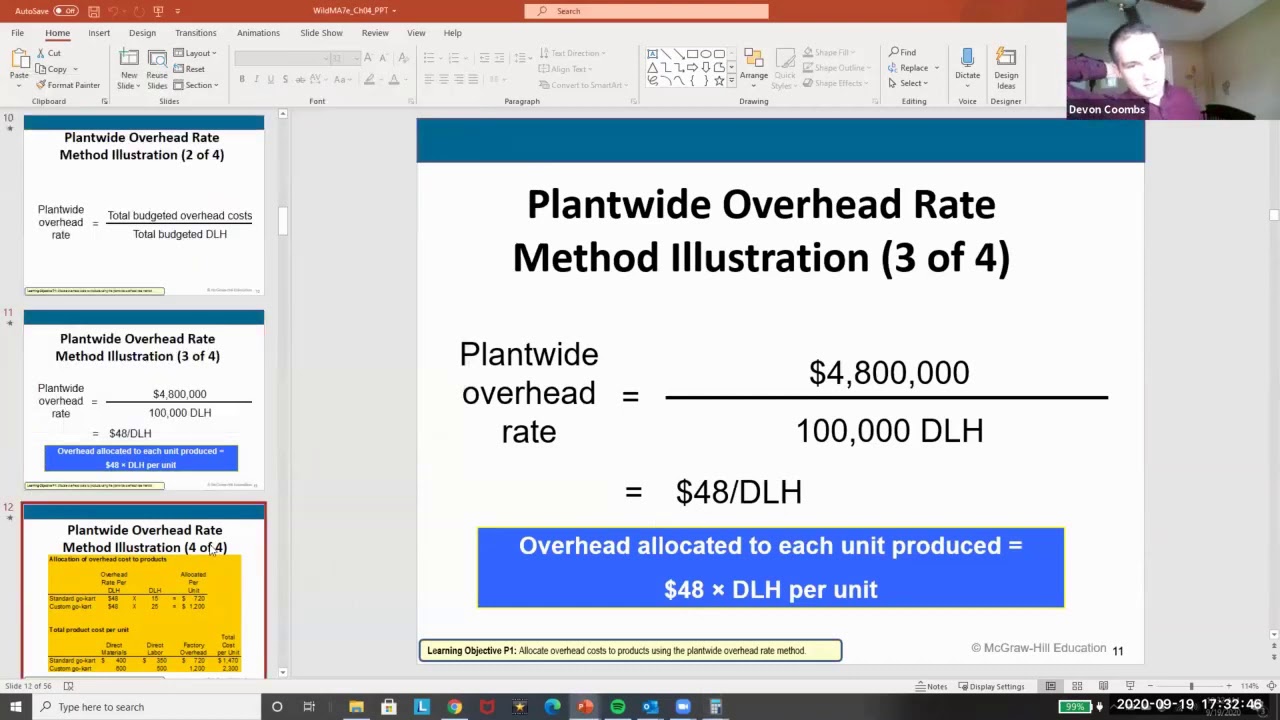
That is, a predetermined overhead rate includes the ratio of the estimated overhead costs for the year to the estimated level of activity for the year. Common examples include machine hours, direct labor hours, or direct materials costs. The choice of allocation base should reflect the principal cause of overhead costs in your operations. A later analysis reveals that the actual amount that should have been assigned to inventory is $48,000, so the $2,000 difference is charged to the cost of goods sold. Using a predetermined overhead rate allows companies to apply manufacturing overhead costs to units produced based on an estimated rate, rather than actual overhead costs. This rate is then used throughout the period and adjusted at year-end if necessary based on actual overhead costs incurred.
Her expertise lies in marketing, economics, finance, biology, and literature. She enjoys writing in these fields to educate and share her wealth of knowledge and experience. Sourcetable is the optimal tool for anyone looking to enhance their efficiency and accuracy in financial analysis or academic learning.
Begin by estimating the total manufacturing overhead costs for a specific period. This could include all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of supervisory staff. This $4 per hour overhead rate would then be applied to the number of direct labor hours for each job to allocate overhead costs.
